What is Community Wellbeing? Conceptual review
Downloads

Intro
This conceptual review pulls together thinking and practice on how to think about and assess community wellbeing.
The primary purpose is to stimulate greater attention and debate to what we are terming ‘being well together’ and how to develop a conceptualisation of community wellbeing.
We envisage two audiences for this review: an academic-oriented audience with an interest in concepts, which may well include policy-makers, and a practitioner or community activist audience with an interest in the potential value of assessing community wellbeing for particular purposes.
State of the evidence
The concept of community wellbeing, as an intermediate scale between the individual and the nation, has the potential to address this neglected aspect of ‘being well together’.
There is a long history of debate about what ‘community’ is. A common distinction is made between territorial and social communities; a community as a residential neighbourhood or as a group of people with shared interests and values, including online communities. We propose using a flexible working definition in which:
Community wellbeing is the combination of social, economic, environmental, cultural, and political conditions identified by individuals and their communities as essential for them to flourish and fulfil their potential.
[Wiseman and Brasher, 2008: 358]
Key findings
Our review found a number of useful concepts and frameworks for community wellbeing and supports the argument that community wellbeing should capture something that is more than the aggregate of individual parts.
If we only aggregate individual assessments, we miss the experience of ‘being well together’ as a key part of our lives, and of community. The exception that does capture the interactive aspects of community is where aggregated individual assessments relate to shared resources, such as the provision of services, the availability of leisure spaces, the sense of safety or belonging and so forth.
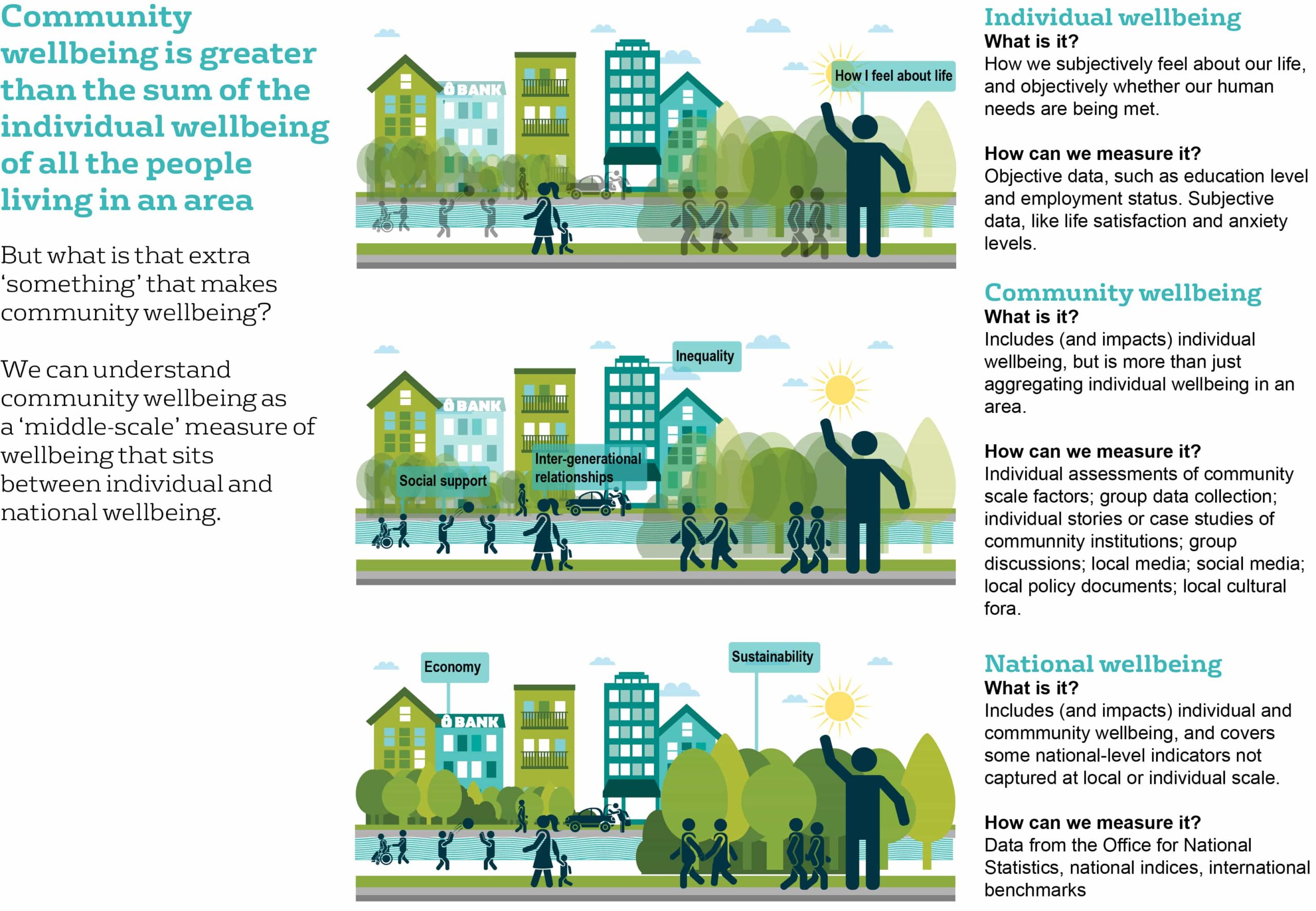
However, we found several important omissions in existing frameworks for community wellbeing.
- Inequality within and between communities undermines claims to community wellbeing and needs to be assessed.
- There is very little attention to intangible cultural heritage that is core to understanding community.
- Local histories are omitted, sustainability or inter-generational relations. This is related to the point above.
- Sustainability- in terms of environment and availability of resources- was only included in two frameworks.
Including these aspects in assessments of community wellbeing will enrich our understandings of ‘being well together’.
Community wellbeing will mean different things in different communities. To help you navigate this, we have developed these questions to help you think through how to conceptualise and capture community wellbeing in your work.
Next steps
The definition we have chosen is a working definition. Over the next year, the Community Wellbeing Evidence Programme will be developing this definition based on the work that we are doing as well as conversations with stakeholders. We would love to hear from you about the following issues:
- Is it useful for your work to conceptualise ‘community wellbeing’ as opposed to just individual wellbeing?
- If so, is the working definition of community wellbeing useful as a starting point? What is missing?
- If you used them, did you find the questions above useful?
- What else is needed to support the conceptualisation of, or development of community wellbeing?
Explore more
Downloads
![]()
[gravityform id=1 title=true description=true ajax=true tabindex=49]
